Disulphide bridges are covalent bonds formed between pairs of cysteine residues (forming cystine). These contribute to the tertiary structure of proteins by linking distant regions of a protein. Disulphide bridges may also occur between different peptide chains within a protein, e.g. between the A and B chains of insulin. They are common in extracellular proteins, but less common in intracellular proteins. Strong reducing agents are required to break the disulphide bridges.
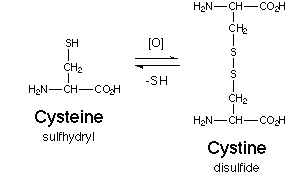 |
| Fig 1: Cysteine and Cystine |
 |
| Fig 1: Disulphide Bridge |
Source: Fig 1, Fig 2, Fig 3,

No comments:
Post a Comment